Time Complexity Intro
Time complexity and Big O notation
Time complexity is a concept used to describe the efficiency of an algorithm based on the time it takes to complete, relative to the size of the input. This helps us compare different algorithms to see which one is more efficient, especially as input sizes grow.
One of the most common ways to express time complexity is with Big O Notation.
What is Big O Notation?
Big O notation is a mathematical way to describe how an algorithm’s runtime grows as the input size increases. It provides an upper bound on the time (or number of steps) required for an algorithm to complete, so we can understand its worst-case scenario.
In Big O notation, we describe the runtime by focusing on the most significant term, ignoring constants and lower-order terms. For example, O(n + 10) simplifies to O(n) because, as n grows, the constant term (10) becomes less significant.
Why Use Big O Notation?
Big O notation allows us to:
- Predict Performance: Understand how an algorithm performs as the input size grows.
- Compare Algorithms: Quickly compare different algorithms based on their efficiency.
- Identify Bottlenecks: Find potential performance issues before they arise.
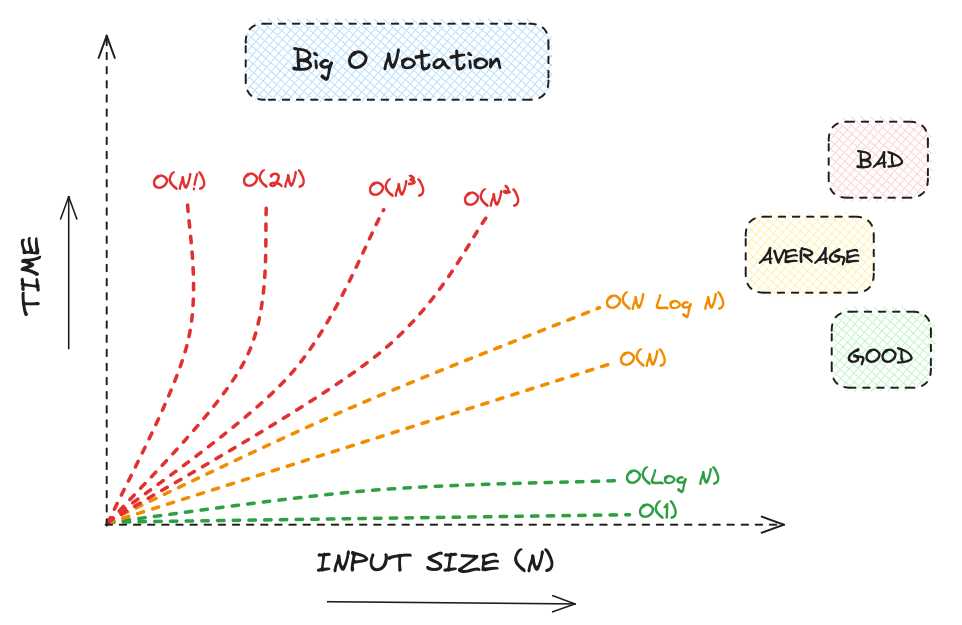
Common Types of Time Complexity
Here are the most common time complexities you'll encounter:
| Complexity | Name | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
O(1) | Constant Time | Accessing an array element |
O(log n) | Logarithmic | Binary search |
O(n) | Linear Time | Simple loop through an array |
O(n log n) | Linearithmic | Efficient sorting (e.g., merge sort) |
O(n²) | Quadratic | Nested loops |
O(2ⁿ) | Exponential | Recursive Fibonacci sequence |
O(n!) | Factorial | Generating all permutations |
Graphical Representation
The following image shows the growth of different time complexities as the input size increases: